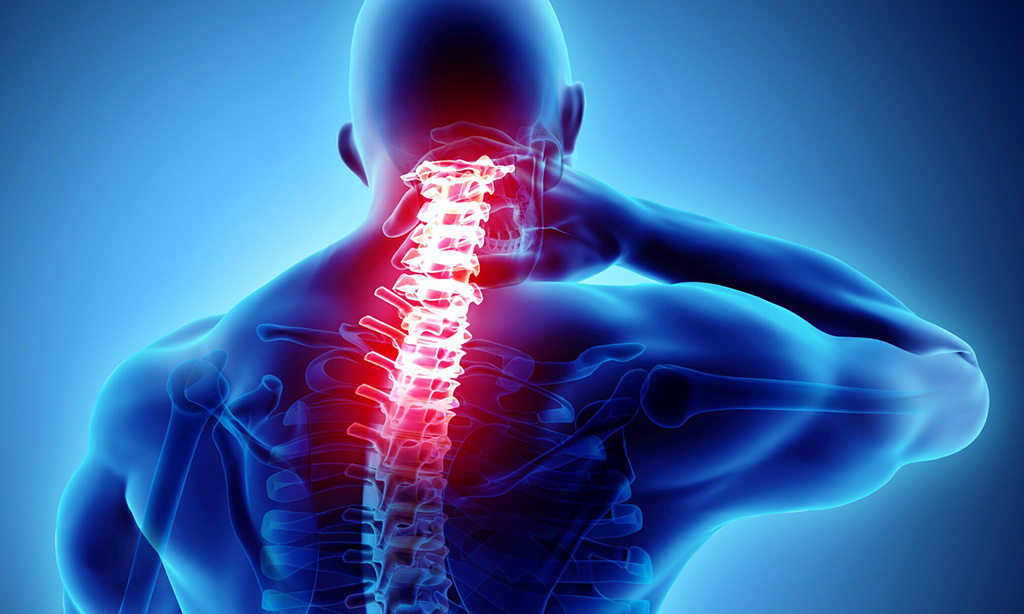
Constant back or neck pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving are often symptoms of spinal arthritis It is a very common but misunderstood condition in the USA. In Miami, Dr. Evan Trapana offers cutting-edge and personalized treatment for patients who are seeking relief from pain, enhanced mobility, and improved quality of life.
Dr. Trapana is committed to offering proven and effective minimally invasive procedures tailored to individual needs. He has many years of ample experience in Spinal care, his expert intervention can make a life-changing difference for you.
It is also known as spinal osteoarthritis, and a worsening condition that impacts the spinal joints, mainly the facet joints and intervertebral discs. With time, the cartilage eases the joints from damage.
Although it can impact people of all ages, this condition is the most common in people older than 50 years. Premature aging, spinal repetitive stress, previous injury, genetics, and obesity are the possible factors for spinal arthritis. Different forms of this condition, such as rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis, can also affect the spine, and often progress more aggressively.
Symptoms of this condition depend on the location and severity. Here we mentioned some possible symptoms that patients usually experience, such as:
As the issue increases, symptoms can disturb daily life routine, such as sleeping, walking, and even standing.
In Miami, Dr. Evan Trapana starts the diagnosis with a complete assessment of medical history and physical examination of patients. He and his team discuss patients’ symptoms, past injuries, or lifestyle. Then Dr. Trapana asses different aspects, such as joint working, spinal alignment, and symptoms of nerve envolvment.
At the end, to complete the diagnosis and the scope of damage, he conducts some cutting-edge imaging tests, such as:
By this complete assessment, he ensures a precise diagnosis that finds the root cause of the problem. Then he and his team suggest a suitable treatment plan to patients for the best possible outcomes.
Dr. Trapana offers a wide range of cutting-edge treatment procedures for spinal arthritis, such as non-surgical and minimally invasive procedures. Here we explain this procedure:
If patients do not get the expected results from a non-surgical procedure, then Dr. Trapana probably suggests minimally invasive procedures, such as:
In severe cases, a minimally invasive surgical procedure is probably considered by Dr. Trapana, such as:
Each surgical procedure is developed with accuracy and concentration on long-term results and patient comfort.
Patients across the USA trust Dr. Evan Trapana because of his expertise and extensive experience in spinal care. Here we mentioned some qualities of Dr. Trapana as a spine surgeon:
Answer: Although it can not be treated completely, it can be effectively handled with the perfect treatment plan. Earlier diagnosis controls further harm and relieves symptoms effectively.
Answer: If you have regular pain in the neck or the lower part of the back, worsening with activities, and same time, feels stiff or reduction in movements, then it can be arthritis of the spine.
Answer: Lifestyle changes, such as staying active, keeping a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and utilizing ergonomic support at work, can greatly relieve symptoms.
Arthritis of Spine Treatment | Arthritis Spine Treatment | Arthritis Lower Spine Treatment | Arthritis in Spine Treatment | Arthritis in Thoracic Spine Treatment