Are you tense because of a degenerated spine, which results in pain and reduced ability to move? Tensed about from where you will get the perfect treatment procedure and surgeon who can help relieve the pain and stiffness due to this condition? You are at the right place where you will come to know the best treatment for spondylosis and an appropriate spine surgeon who can offer effective results of the treatment. Dr. Evan Trapana is renowned for offering the best spinal treatments in Miami, Florida. He and his team use innovative surgical methods that can help the patient get relief from the discomfort of spondylosis. If you or someone you know is struggling with this condition, you can either visit Miami or book your appointment.
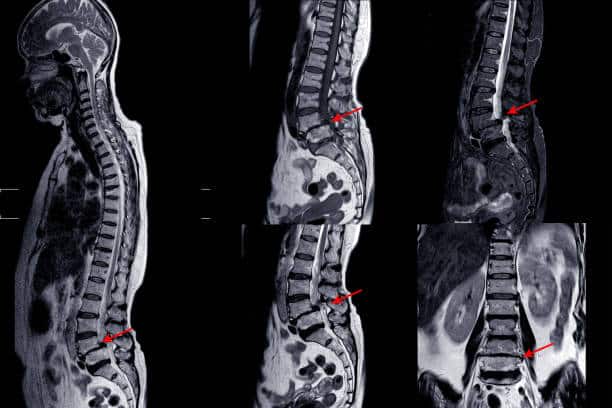
Spondylosis is a condition in which the age-related degeneration of the spine occurs, and damage to the vertebrae, joints, and discs. This condition can lead to pain and reduced ability to move and walk. Spondylosis is a serious and worsening condition that affects people after the age of 60.
Different types of spondylosis that can affect the spine, include cervical spondylosis (affects the neck), thoracic spondylosis (affects mid-back), lumbar spondylosis (affects lower back), and multilevel spondylosis (affects the multiple areas of the spine).
The treatment for the spondylosis can be performed by considering the complexity of the condition and the overall health of the patient. Here are some treatments available for spondylosis:
After spondylosis treatment, one needs to focus on light exercises that can help in back straightening. The individual needs to maintain a good posture and can use ergonomic chairs for this. Maintaining a healthy diet and hydration are a must to keep your spinal discs healthy. If you smoke, then you need to quit smoking, as smoking can lead to cause damage to the spinal discs.
Cervical Spondylosis is a medical condition for which various treatments and procedures are available. If cervical spondylosis is treated early, then it can show effective results in the spine. Surgical and non-surgical treatments are available for this condition. If there is no relief from the conservative treatment procedures, then surgery is a considerable option for spondylosis. You can choose Dr. Evan Trapana for spondylosis treatment, as he specializes in offering reliable treatment methods with personalized care and has experience in performing 2000+ successful spine surgeries.
Answer. The symptoms of spondylosis can include pain, discomfort, weakness, neck stiffness, pain in the lower back, and a less flexible spine. In severe cases, one may feel difficulty in walking and balancing. When an individual feels the bladder control, then this condition needs urgent medical attention.
Answer. After the spondylosis treatment, you need to take rest for a few weeks. You can return to your work within a few days, it generally depends on your overall health for faster recovery.
Answer. The requirement for the diagnosis of spondylosis may include, medical history of the patient. The doctor may perform some imaging tests, including X-rays and CT scans, that can visualise the detailed images of the spine. A physical examination is also performed by the surgeon to check the overall health of the patient.
Answer. Surgical treatment is generally recommended in complex cases and when non-conservative methods are performed, but no relief from the pain and discomfort from spondylosis is observed.
Cervical Spondylosis Treatment | Cervical Spondylosis C5-C6 Treatment | Cervical Spondylosis C5 C6 Treatment |Treatment For Cervical Spondylosis | Cervical Spine Spondylosis Treatment